Irénee Aubry: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Irénee Aubry was an inventor and watchmaker originally from [[Muriaux]] but working in [[La Chaux-de-Fonds]] throughout his career. | Irénee Aubry was an inventor and watchmaker originally from [[Muriaux]] but working in [[La Chaux-de-Fonds]] throughout his career. Aubry was best known for his invention of the 8-day pocket watch known as [[Hebdomas]], which remains in production over 100 years later. He previously created a 40-day watch for Pope Leo XIII, establishing his reputation in the industry. | ||
==Early Life== | |||
Paul-Joseph-Irénee Aubry was born in Muriaux, Switzerland about [[1859]]. This small village was located in the [[Jura Triangle]] close to [[Saignelégier]], north of [[La Chaux-de-Fonds]] in the [[Franches-Montagnes]] region of the [[Swiss Jura]]. He was commonly called Irénee Aubry, with his first name often spelled Irénée later in life. His father was likely Victor Aubry (1830?-May 30, 1898), and his siblings were likely Mrs. Boniface Girardin-Aubry, Paul Aubry, and Mrs. Alcide Taillard-Aubry. | |||
Around [[1882]] Irénee Aubry married Elisa-Marie Jeandupeux, also spelled Jean-du-Peux ([[1863]]-[[1937]]). The couple is said to have had 14 children, all of whom became involved in the watchmaking trade. Their surviving sons notably include [[F. Aubry-Schaltenbrand|Virgile-Francis]] and [[A. Aubry-Gostely|Arthur-François]] who founded their own watchmaking businesses like their father. | |||
Aubry | Working in Saignelégier, Aubry was known locally as "the inventor", which was meant both as praise for his mind and as criticism of his lack of business success. He was fixated on long power reserve watches and became a pioneer in the field. In the mid 1880s he created a watch movement that could run for 40 days without winding. He immediately took out patents in several foreign countries (we know of Spanish patent 5806 "Un nuevo reloj llamado de cuarenta días"), and was waiting for patents to be established in Switzerland as well. He also claimed to have created a watch that could run for three months, though the details of this mechanism were kept secret. | ||
==Pope Leo XIII's 40-Day Watch== | |||
[[File:L'Impartial 1998-04-21-017-000 images.jpg|right|400px]] | |||
With Pope Leo XIII celebrating the 50th anniversary of his ordination in [[1887]], the deanery of Franches-Montagnes commissioned a fine watch to be presented to the Sovereign Pontiff. Aubry's 40-day movement was a natural expression of the capability of the region, and the 29 year old watchmaker was selected to provide the movement. The result was a fine 63 mm pocket watch cased in 18 karat gold. The back was engraved with the Pope's arms and the pontifical emblem around a beautiful painted enamel portrait of the pope, signed by Champod. The dial was made of white enamel with faux green enameled cartouches and Arabic numerals and gold pear-shaped hands. | |||
But the most notable aspect of this fine watch was Aubry's 40-day movement, a feat never before accomplished. In addition to the incredible power reserve, Aubry's movement featured central seconds, crown winding, a lateral anchor and cut bimetallic balance, and Breguet hairspring. He built the movement in nickel with a sun decoration, 23 jewels, and screwed gold chatons. Although the movement itself was just 16 ligne in diameter, the large main spring, situated coaxially directly under the dial, was 43 mm across. | |||
Although widely forgotten after it was presented, the watch caused a stir in [[1982]] when it was sold by Antiquorum in Geneva to an Italian buyer for 120,000 francs. It reappeared again at [[BaselWorld|Basel 98]], and the publicity there triggered the rediscovery of Aubry's prototype movement in the collection of the watchmaking museum in the French city of Villers-le-Lac. Although the watch remains in private hands, this prototype is on display at the museum to this day. | |||
The watch established Aubry's reputation as an inventor and watchmaker, enabling the young family to move to the watchmaking city of [[La Chaux-de-Fonds]] to pursue the trade. He soon set about applying his ideas to a more practical watch. | |||
==Hebdomas== | |||
[[File:CH 88 A-3.png|right|200px]] | |||
[[File:CH 2 E-3.png|right|200px]] | |||
Aubry applied his work on long power reserve movements to a practical 8-day pocket watch movement. The resulting design was quite novel in that it effectively flipped the entire movement inside the case: Rather than locating the large coaxial mainspring barrel between the movement and dial, Aubry drove the hands from the "back" of the movement using an off-center pinion close to the crown, locating the mainspring at the back of the case. Since the balance was the thickest part of the movement and was located opposite the crown at the [[Lépine]] location, Aubry thought to cut out the dial and expose the moving balance through an aperture of the dial. | |||
On May 20, [[1888]], Paul-Joseph-Irénée Aubry of Muriaux, Célestin-Arthur Graizely of la Ferrière, and Joseph-Ariste Godat of Les Bois formed a company called Aubry, Graizely & Godat in la Ferrière, to commercialize Aubry's design. This firm was located closer to La Chaux-de-Fonds on the road from Saignelégier and was the home of Graizely, who would capitalize on Aubry's design more than anyone else. And the formation of the company coincided with the news that Switzerland would finally open a patent office to protect inventions like Aubry's. | |||
The original design was drawn up for Swiss patent protection on November 14, [[1888]], the day the patent office opened, submitted five days later, and was published as CH88 on January 10, [[1889]]. An addendum was registered on January 21, [[1889]], officially called CH88/2. This patent was also dated November 14, 1888, and covered the basic design on the Hebdomas watch, including the open dial showing the balance mounted on a straight-across bridge and, notably, driving the full-diameter mainspring barrel using teeth around the circumference rather than a pivot at the center. This technique, of driving the mainspring barrel directly using teeth and a ratchet around the circumference, would become standard in most watches, though the unusually large barrel of the Hebdomas is notable. | |||
Aubry's invention of the 8-day pocket watch was a significant technical feat at the time. He filed three patents in 1888, 1890, and 1892 to protect his invention. The watches he created gained recognition and success, with his invention receiving an honorable mention at the Geneva Exhibition. | |||
The patent changed hands quickly: On February 17, 1889, patent CH88/2 was reassigned by Irénee Aubry to Aubry, Graizely, & Godat. Aubry formed a joint venture with Saignelégier watchmaker François Froidevaux on May 1, [[1890]] called Aubry & Froidevaux and left the partnership with Graizely and Godat on May 15, [[1891]], leaving patent CH88/2 to Aubry alone, as noted on June 2. Just 6 days later, Aubry licensed the patent to Ariste Godat, François Froidevaux, and Arthur Graizely. Finally, on December 1, Aubry & Froidevaux was dissolved, becoming F. Froidevaux alone. Froidevaux's company was dissolved on March 13, [[1901]], following his death. Ariste Godat's firm was dissolved on August 8, [[1911]]. | The patent changed hands quickly: On February 17, 1889, patent CH88/2 was reassigned by Irénee Aubry to Aubry, Graizely, & Godat. Aubry formed a joint venture with Saignelégier watchmaker François Froidevaux on May 1, [[1890]] called Aubry & Froidevaux and left the partnership with Graizely and Godat on May 15, [[1891]], leaving patent CH88/2 to Aubry alone, as noted on June 2. Just 6 days later, Aubry licensed the patent to Ariste Godat, François Froidevaux, and Arthur Graizely. Finally, on December 1, Aubry & Froidevaux was dissolved, becoming F. Froidevaux alone. Froidevaux's company was dissolved on March 13, [[1901]], following his death. Ariste Godat's firm was dissolved on August 8, [[1911]]. | ||
These confusing transactions likely left Aubry with money to pursue his watchmaking inventions even as others would profit from his Hebdomas design. | |||
==Later Life== | |||
Aubry's workshop was at Rue du Grenier 24 in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had a branch in Villers-le-Lac by [[1906]]. At this time the company specialized in watches with a visible balance based on Aubry's patent. They produced watches with 8, 15, and 30 days power reserve in sizes from 14 to 20 ligne and 30 and 42 ligne, including some with central seconds. | Aubry's workshop was at Rue du Grenier 24 in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had a branch in Villers-le-Lac by [[1906]]. At this time the company specialized in watches with a visible balance based on Aubry's patent. They produced watches with 8, 15, and 30 days power reserve in sizes from 14 to 20 ligne and 30 and 42 ligne, including some with central seconds. | ||
Aubry's talent and skill as a watchmaker were highly regarded, and he was known as "the inventor" in his hometown of Franches-Montagnes. He was dedicated to his craft and always sought to push the boundaries of watchmaking. He continued to refine his inventions and claimed to have created a watch that could run for three months, although the details of this mechanism remained known only to him. | |||
Despite his success as an inventor, Aubry was not motivated by money. He was driven by a desire to innovate and create exceptional timepieces. His contributions to the watchmaking industry were highly regarded, and his inventions left a lasting impact. | |||
Aubry's legacy lives on through his descendants, who have carefully preserved the pontifical decoration and diploma that accompanied the watch he made for Pope Leo XIII. Although few people have had the privilege of seeing the legendary watch that crowned Aubry's career, his achievements continue to be celebrated in the watchmaking world. | |||
The Aubry family moved to Chez-le-Bart on the shores of Lake Neuchâtel near Gorgier-Saint-Aubin in [[1911]] and moved the business there. At this point the company still produced watches with 8, 15, or 30 days power reserve in 11 or 18 line sizes, including an ultra-slim watch. Aubry's son Francis Aubry-Schaltenbrand registered [[F. Aubry-Schaltenbrand|his own watchmaking business]] in La Chaux-de-Fonds on January 24 of that year, with Arthur Aubry joining management in 1917. This business failed and was closed on February 26, [[1920]]. | The Aubry family moved to Chez-le-Bart on the shores of Lake Neuchâtel near Gorgier-Saint-Aubin in [[1911]] and moved the business there. At this point the company still produced watches with 8, 15, or 30 days power reserve in 11 or 18 line sizes, including an ultra-slim watch. Aubry's son Francis Aubry-Schaltenbrand registered [[F. Aubry-Schaltenbrand|his own watchmaking business]] in La Chaux-de-Fonds on January 24 of that year, with Arthur Aubry joining management in 1917. This business failed and was closed on February 26, [[1920]]. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 64: | ||
*** Félix Schaltenbrand of Paris | *** Félix Schaltenbrand of Paris | ||
*** Georges Schaltenbrand of Paris | *** Georges Schaltenbrand of Paris | ||
** | ** Marie-Cécile-Elzire Aubry (January 13, 1889-October 1962) married 1914 watchmaker and optician Charles-Jacques von Gunten (November 29, 1883 and died July 12, 1955) - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds | ||
*** Charles von Gunten-Jeanneret | *** Charles von Gunten-Jeanneret married 1946 Marguerite-Alice Jeanneret | ||
**** Anne-Marie | **** Anne-Marie | ||
**** Charles-André | **** Charles-André (March 18, 1949-) | ||
**** Claudine | **** Claudine | ||
*** may also have been related to René von Gunten-Aubry | *** may also have been related to René von Gunten-Aubry | ||
** Irène Müller-Aubry (born about 1890 and died July 7, 1982) married Robert Müller - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds | ** Irène Müller-Aubry (born about 1890 and died July 7, 1982) married Robert Müller - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds | ||
** Arthur Aubry-Gostely (born about 1891 and died December 28, 1984) - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had children | ** [[A. Aubry-Gostely|Arthur-François Aubry-Gostely]] (born about 1891 and died December 28, 1984) married 1920 Marguerite-Agnès Gostely - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had children | ||
** Victoria-Alice Perrenoud-Aubry (known as Alice Perrenoud-Aubry, born late October 1892) married Edmond Perrenoud - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had children | ** Victoria-Alice Perrenoud-Aubry (known as Alice Perrenoud-Aubry, born late October 1892) married Edmond Perrenoud - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had children | ||
** Marc-Albert ( | ** Marc-Albert Aubry (April 24, 1894-July 24, 1918) married June 29, 1916 Jeanne-Marguerite Novelli | ||
** Léon-Abel | ** Léon-Abel "Abel" Aubry (May 22, 1895-November 11, 1955) - watchmaker in La Chaux-de-Fonds | ||
** Charles-Louis (a baby born May 28, 1896 and died June 26) | ** Charles-Louis (a baby born May 28, 1896 and died June 26) | ||
** Henri Aubry-Brancher ( | ** Henri-Emile Aubry-Brancher (1903-April 12, 1985) married August 9, 1928 Héléne Tissot, later married Héloïse-Marie-Madeline-Jeanne Brancher - lived in Algeria | ||
** Mrs. Charles Gascard-Aubry - lived in Berne and had children | ** Mrs. Charles Gascard-Aubry - lived in Berne and had children | ||
==Patents== | ==Patents== | ||
* CH34981 - Pendulette à huit jours de marche | * ES5806A1, March 30, 1886 - "Un nuevo reloj llamado de cuarenta días" - Patent for 40-day movement used in Pope Leo XIII watch | ||
* CH39165, March 11, 1907 - Fond de boite de montre | * CH88, January 10, 1889 - "Nouvelle disposition du mécanisme des montres de toutes dimensious particulièrement applieable aux montres bijoux et ans montres marchant huit jours et plus" - Aubry's original 8-day movement with center winding | ||
* CH40663, November 21, 1907 - Mouvement de montre | ** CH88/2, January 21, 1889 - "Nouvelle disposition du mécanisme des montres de toutes dimensions particulièrement applicable aux montres-bijoux et aux montres marchant 8 jours et plus" - Aubry's Hebdomas patent with peripheral winding | ||
* CH44117, April 29, 1908 - Montre | * CH5741, October 15, 1892 - "Combinaison de rouages à grosse denture pour montres de petit calibre" - deleted January 1896 | ||
* CH54707, January 13, 1911 - Mouvement de montre à marche de longue durée | * Dessin 8161, September 4, 1901 - 3 modèles - montres - deleted November 1906 | ||
* CH75676, November 23, 1916 - Montre à barillet fixe | * CH27545, February 3, 1903 - "Montre à longue marche perfectionnée" - A different 8-day watch movement design - deleted May 1905 | ||
* CH28100, March 30, 1903 - "Montre à longue marche perfectionnée" - An update to the Hebdomas patent - deleted July 1908 | |||
** CH28100/470, March 14, 1904 - "Montre à longue marche perfectionnée" - An update to the Hebdomas patent - deleted July 1908 | |||
* CH34981, November 1, 1905 - "Pendulette à huit jours de marche" - An 8-day clock with exposed balance - deleted February 1908 | |||
** FR370766, October 25, 1906 - "Pendulette à huit jours de marche" - French registration | |||
* CH39165, March 11, 1907 - "Fond de boite de montre" - licensed to [[Société Horlogére Reconvilier]] on April 18, 1908, deleted June 1908 | |||
* CH40663, November 21, 1907 - "Mouvement de montre" - An extra-thin watch movement - deleted February 1912 | |||
** FR395170, October 12, 1908 - "Mouvement de montre" - French registration | |||
* CH44117, April 29, 1908 - "Montre" - A different movement with a central mainspring barrel and exposed balance - deleted August 1909 | |||
* CH54707, January 13, 1911 - "Mouvement de montre à marche de longue durée" - A different movement with a central mainspring barrel - deleted July 1912 | |||
* CH75676, November 23, 1916 - "Montre à barillet fixe" - A long-duration movement with a mainspring fixed in the case around the movement | |||
==See Also== | |||
* [[F. Aubry-Schaltenbrand]] ([[Abra]] and [[Brota]]) | |||
* [[A. Aubry-Gostely]] ([[Gindrat-Delachaux]] and [[Brigos]]) | |||
[[Category:Biography A]] | [[Category:Biography A|Aubry, Irénee]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:21, 13 January 2024
Irénee Aubry was an inventor and watchmaker originally from Muriaux but working in La Chaux-de-Fonds throughout his career. Aubry was best known for his invention of the 8-day pocket watch known as Hebdomas, which remains in production over 100 years later. He previously created a 40-day watch for Pope Leo XIII, establishing his reputation in the industry.
Early Life
Paul-Joseph-Irénee Aubry was born in Muriaux, Switzerland about 1859. This small village was located in the Jura Triangle close to Saignelégier, north of La Chaux-de-Fonds in the Franches-Montagnes region of the Swiss Jura. He was commonly called Irénee Aubry, with his first name often spelled Irénée later in life. His father was likely Victor Aubry (1830?-May 30, 1898), and his siblings were likely Mrs. Boniface Girardin-Aubry, Paul Aubry, and Mrs. Alcide Taillard-Aubry.
Around 1882 Irénee Aubry married Elisa-Marie Jeandupeux, also spelled Jean-du-Peux (1863-1937). The couple is said to have had 14 children, all of whom became involved in the watchmaking trade. Their surviving sons notably include Virgile-Francis and Arthur-François who founded their own watchmaking businesses like their father.
Working in Saignelégier, Aubry was known locally as "the inventor", which was meant both as praise for his mind and as criticism of his lack of business success. He was fixated on long power reserve watches and became a pioneer in the field. In the mid 1880s he created a watch movement that could run for 40 days without winding. He immediately took out patents in several foreign countries (we know of Spanish patent 5806 "Un nuevo reloj llamado de cuarenta días"), and was waiting for patents to be established in Switzerland as well. He also claimed to have created a watch that could run for three months, though the details of this mechanism were kept secret.
Pope Leo XIII's 40-Day Watch
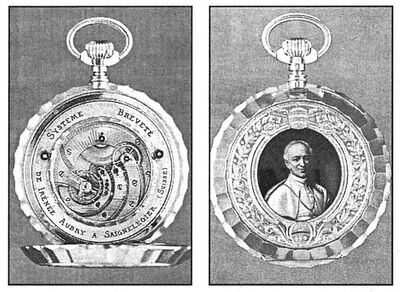
With Pope Leo XIII celebrating the 50th anniversary of his ordination in 1887, the deanery of Franches-Montagnes commissioned a fine watch to be presented to the Sovereign Pontiff. Aubry's 40-day movement was a natural expression of the capability of the region, and the 29 year old watchmaker was selected to provide the movement. The result was a fine 63 mm pocket watch cased in 18 karat gold. The back was engraved with the Pope's arms and the pontifical emblem around a beautiful painted enamel portrait of the pope, signed by Champod. The dial was made of white enamel with faux green enameled cartouches and Arabic numerals and gold pear-shaped hands.
But the most notable aspect of this fine watch was Aubry's 40-day movement, a feat never before accomplished. In addition to the incredible power reserve, Aubry's movement featured central seconds, crown winding, a lateral anchor and cut bimetallic balance, and Breguet hairspring. He built the movement in nickel with a sun decoration, 23 jewels, and screwed gold chatons. Although the movement itself was just 16 ligne in diameter, the large main spring, situated coaxially directly under the dial, was 43 mm across.
Although widely forgotten after it was presented, the watch caused a stir in 1982 when it was sold by Antiquorum in Geneva to an Italian buyer for 120,000 francs. It reappeared again at Basel 98, and the publicity there triggered the rediscovery of Aubry's prototype movement in the collection of the watchmaking museum in the French city of Villers-le-Lac. Although the watch remains in private hands, this prototype is on display at the museum to this day.
The watch established Aubry's reputation as an inventor and watchmaker, enabling the young family to move to the watchmaking city of La Chaux-de-Fonds to pursue the trade. He soon set about applying his ideas to a more practical watch.
Hebdomas
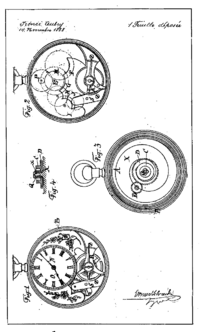
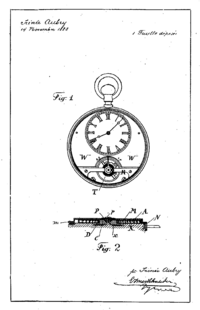
Aubry applied his work on long power reserve movements to a practical 8-day pocket watch movement. The resulting design was quite novel in that it effectively flipped the entire movement inside the case: Rather than locating the large coaxial mainspring barrel between the movement and dial, Aubry drove the hands from the "back" of the movement using an off-center pinion close to the crown, locating the mainspring at the back of the case. Since the balance was the thickest part of the movement and was located opposite the crown at the Lépine location, Aubry thought to cut out the dial and expose the moving balance through an aperture of the dial.
On May 20, 1888, Paul-Joseph-Irénée Aubry of Muriaux, Célestin-Arthur Graizely of la Ferrière, and Joseph-Ariste Godat of Les Bois formed a company called Aubry, Graizely & Godat in la Ferrière, to commercialize Aubry's design. This firm was located closer to La Chaux-de-Fonds on the road from Saignelégier and was the home of Graizely, who would capitalize on Aubry's design more than anyone else. And the formation of the company coincided with the news that Switzerland would finally open a patent office to protect inventions like Aubry's.
The original design was drawn up for Swiss patent protection on November 14, 1888, the day the patent office opened, submitted five days later, and was published as CH88 on January 10, 1889. An addendum was registered on January 21, 1889, officially called CH88/2. This patent was also dated November 14, 1888, and covered the basic design on the Hebdomas watch, including the open dial showing the balance mounted on a straight-across bridge and, notably, driving the full-diameter mainspring barrel using teeth around the circumference rather than a pivot at the center. This technique, of driving the mainspring barrel directly using teeth and a ratchet around the circumference, would become standard in most watches, though the unusually large barrel of the Hebdomas is notable.
Aubry's invention of the 8-day pocket watch was a significant technical feat at the time. He filed three patents in 1888, 1890, and 1892 to protect his invention. The watches he created gained recognition and success, with his invention receiving an honorable mention at the Geneva Exhibition.
The patent changed hands quickly: On February 17, 1889, patent CH88/2 was reassigned by Irénee Aubry to Aubry, Graizely, & Godat. Aubry formed a joint venture with Saignelégier watchmaker François Froidevaux on May 1, 1890 called Aubry & Froidevaux and left the partnership with Graizely and Godat on May 15, 1891, leaving patent CH88/2 to Aubry alone, as noted on June 2. Just 6 days later, Aubry licensed the patent to Ariste Godat, François Froidevaux, and Arthur Graizely. Finally, on December 1, Aubry & Froidevaux was dissolved, becoming F. Froidevaux alone. Froidevaux's company was dissolved on March 13, 1901, following his death. Ariste Godat's firm was dissolved on August 8, 1911.
These confusing transactions likely left Aubry with money to pursue his watchmaking inventions even as others would profit from his Hebdomas design.
Later Life
Aubry's workshop was at Rue du Grenier 24 in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had a branch in Villers-le-Lac by 1906. At this time the company specialized in watches with a visible balance based on Aubry's patent. They produced watches with 8, 15, and 30 days power reserve in sizes from 14 to 20 ligne and 30 and 42 ligne, including some with central seconds.
Aubry's talent and skill as a watchmaker were highly regarded, and he was known as "the inventor" in his hometown of Franches-Montagnes. He was dedicated to his craft and always sought to push the boundaries of watchmaking. He continued to refine his inventions and claimed to have created a watch that could run for three months, although the details of this mechanism remained known only to him.
Despite his success as an inventor, Aubry was not motivated by money. He was driven by a desire to innovate and create exceptional timepieces. His contributions to the watchmaking industry were highly regarded, and his inventions left a lasting impact.
Aubry's legacy lives on through his descendants, who have carefully preserved the pontifical decoration and diploma that accompanied the watch he made for Pope Leo XIII. Although few people have had the privilege of seeing the legendary watch that crowned Aubry's career, his achievements continue to be celebrated in the watchmaking world.
The Aubry family moved to Chez-le-Bart on the shores of Lake Neuchâtel near Gorgier-Saint-Aubin in 1911 and moved the business there. At this point the company still produced watches with 8, 15, or 30 days power reserve in 11 or 18 line sizes, including an ultra-slim watch. Aubry's son Francis Aubry-Schaltenbrand registered his own watchmaking business in La Chaux-de-Fonds on January 24 of that year, with Arthur Aubry joining management in 1917. This business failed and was closed on February 26, 1920.
Irénee Aubry and his wife celebrated their golden wedding anniversary in La Chaux-de-Fonds at a family reunion in April 1932. The couple had retired to Saint-Aubin. Irénee Aubry died on January 20, 1936 in Chez-le-Bart, and Elise-Marie Jeandupeux died on January 25, 1937.
Family
- Paul-Joseph-Irénee Aubry (about 1859-January 20, 1936) married Elisa-Marie Jeandupeux, also spelled Jean du Peux (November 2, 1863-January 25, 1937)
- Eva Aubry (July 19, 1882-December 17, 1951) - lived in Chez-le-Bart in 1936
- René Aubry-Rey (about 1885-December 4, 1959) married about 1909 Marthe Rey (died after 1976) - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds
- René Aubry-Bertrand
- Mrs. Eugène Frangière-Aubry
- Albert Aubry-Krebs
- Virgile-Francis Aubry (about 1888-July 19, 1976) married Eugénie Schaltenbrand (died August 19, 1936) and on December 10, 1937 married Marguerite Hostettler - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had children and grandchildren - watchmaker at Rue Léopold-Robert 74 (later 90), La Chaux-de-Fonds, from 1911 to 1920
- René Aubry - lived in Berne
- Jean-Pierre
- Francine Aubry
- Félix Schaltenbrand of Paris
- Georges Schaltenbrand of Paris
- René Aubry - lived in Berne
- Marie-Cécile-Elzire Aubry (January 13, 1889-October 1962) married 1914 watchmaker and optician Charles-Jacques von Gunten (November 29, 1883 and died July 12, 1955) - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds
- Charles von Gunten-Jeanneret married 1946 Marguerite-Alice Jeanneret
- Anne-Marie
- Charles-André (March 18, 1949-)
- Claudine
- may also have been related to René von Gunten-Aubry
- Charles von Gunten-Jeanneret married 1946 Marguerite-Alice Jeanneret
- Irène Müller-Aubry (born about 1890 and died July 7, 1982) married Robert Müller - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds
- Arthur-François Aubry-Gostely (born about 1891 and died December 28, 1984) married 1920 Marguerite-Agnès Gostely - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had children
- Victoria-Alice Perrenoud-Aubry (known as Alice Perrenoud-Aubry, born late October 1892) married Edmond Perrenoud - lived in La Chaux-de-Fonds and had children
- Marc-Albert Aubry (April 24, 1894-July 24, 1918) married June 29, 1916 Jeanne-Marguerite Novelli
- Léon-Abel "Abel" Aubry (May 22, 1895-November 11, 1955) - watchmaker in La Chaux-de-Fonds
- Charles-Louis (a baby born May 28, 1896 and died June 26)
- Henri-Emile Aubry-Brancher (1903-April 12, 1985) married August 9, 1928 Héléne Tissot, later married Héloïse-Marie-Madeline-Jeanne Brancher - lived in Algeria
- Mrs. Charles Gascard-Aubry - lived in Berne and had children
Patents
- ES5806A1, March 30, 1886 - "Un nuevo reloj llamado de cuarenta días" - Patent for 40-day movement used in Pope Leo XIII watch
- CH88, January 10, 1889 - "Nouvelle disposition du mécanisme des montres de toutes dimensious particulièrement applieable aux montres bijoux et ans montres marchant huit jours et plus" - Aubry's original 8-day movement with center winding
- CH88/2, January 21, 1889 - "Nouvelle disposition du mécanisme des montres de toutes dimensions particulièrement applicable aux montres-bijoux et aux montres marchant 8 jours et plus" - Aubry's Hebdomas patent with peripheral winding
- CH5741, October 15, 1892 - "Combinaison de rouages à grosse denture pour montres de petit calibre" - deleted January 1896
- Dessin 8161, September 4, 1901 - 3 modèles - montres - deleted November 1906
- CH27545, February 3, 1903 - "Montre à longue marche perfectionnée" - A different 8-day watch movement design - deleted May 1905
- CH28100, March 30, 1903 - "Montre à longue marche perfectionnée" - An update to the Hebdomas patent - deleted July 1908
- CH28100/470, March 14, 1904 - "Montre à longue marche perfectionnée" - An update to the Hebdomas patent - deleted July 1908
- CH34981, November 1, 1905 - "Pendulette à huit jours de marche" - An 8-day clock with exposed balance - deleted February 1908
- FR370766, October 25, 1906 - "Pendulette à huit jours de marche" - French registration
- CH39165, March 11, 1907 - "Fond de boite de montre" - licensed to Société Horlogére Reconvilier on April 18, 1908, deleted June 1908
- CH40663, November 21, 1907 - "Mouvement de montre" - An extra-thin watch movement - deleted February 1912
- FR395170, October 12, 1908 - "Mouvement de montre" - French registration
- CH44117, April 29, 1908 - "Montre" - A different movement with a central mainspring barrel and exposed balance - deleted August 1909
- CH54707, January 13, 1911 - "Mouvement de montre à marche de longue durée" - A different movement with a central mainspring barrel - deleted July 1912
- CH75676, November 23, 1916 - "Montre à barillet fixe" - A long-duration movement with a mainspring fixed in the case around the movement